According to Statista, in December 2021, Android held a leading position among the mobile operating systems worldwide with the largest market share, 70 percent, while the runner-up, iOS, had settled for 29 percent of the mobile operating system market.
Mobile operating systems’ market share worldwide
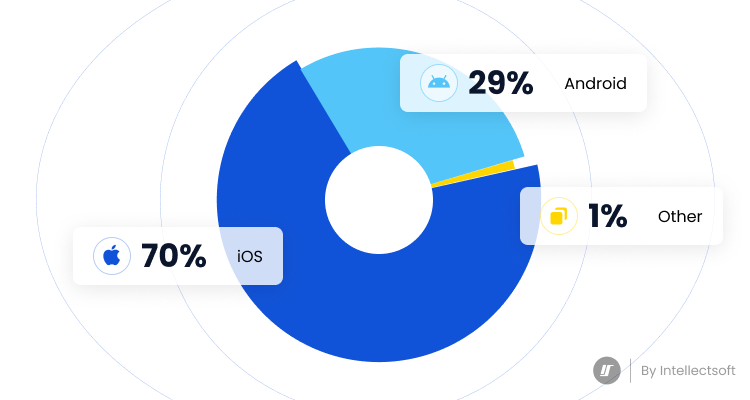
This top position is stipulated by the number of mobile device owners who are more likely to use Android over iOS is increasing every day as the first OS is primarily known for its affordable price range.
The mobile app development industry is thriving and app usage is still growing at a steady rate. Apparently, the future of Android app development is solid as smartphone shipments are projected to reach 1.41 billion in 2022. Android apps are being released more often than iOS applications. At present, 2.56 million apps are available for Android users to install, while iOS offers no more than 1.85 million applications.
However, the app’s success depends on its high level of performance, speed, and reactivity. And choosing the right development tools has a big effect on the project’s efficiency. Therefore, software engineers need to take full advantage of tools like frameworks and libraries to develop fast and high-quality Android apps. And learning the variety of the top frameworks for Android app development is the first step towards the progress of your project.
What is an app framework? What types of app frameworks do exist?
An app framework is a software platform that provides the templates, components, and structure to support the building of applications with a view to reducing common problems encountered in development. Applying code that is shared across modules helps engineers achieve this purpose. Simply put, frameworks act as layouts for app development projects.
In terms of how applications work on a phone device, app frameworks are divided into the following categories: native, web, and hybrid apps. Let’s dive into their main characteristics, purpose, and find out the differences between ways of app development to help you understand which variant is the best for you.
Native applications
Typically, built native applications are created for a specific OS like Android, Windows, etc. using appropriate programming languages. Accessing built-in functions like Bluetooth, microphone, GPS, NFC, etc. this type of app uses the device’s services to operate faster, which leads to an enhanced user experience.
Web applications
Basically, these apps operate through a web browser on the smartphone. With PWA, only one version is being developed, which works for iOS as well as Android. One of the key benefits of this approach is the fact that it is cheaper and faster to develop compared to the previous type of app. Besides, it doesn’t require efforts for maintenance and updating.
Hybrid applications
Representing a mix of the above apps, hybrid apps are built from one codebase for all devices. Engineers are not limited to one platform; instead, they can create an app that will work with multiple platforms, which enables cost and resource reductions. Unlike native apps, hybrid applications lack speed and performance.
Time for a MarTech health check
Is your MarTech stack fueling growth or wasting budget? Spot the issues and fix them fast with this free guide from the experts at ConsultMyApp.
Download nowAlso, you can read the recent study that talks about the differences between hybrid and native app development, their main pros and cons, and other characteristics that will help you understand when you should go for native and in what cases hybrid application development is an optimal solution.
Why is it important to use a framework?
Acting as the fundamental building blocks that are used as the structure of a particular application, frameworks were designed to reduce the need to perform repetitive tasks over and over again. They represent a set of templates and libraries that dictate the architecture of an application and help programmers build software. Thus, frameworks provide functionality with no need to create it from scratch, saving time and development costs.
Top 5 Android frameworks and their key features
React Native
Based on JavaScript, React Native is the most popular framework that is applied for both Android and iOS mobile application development. Although React was also developed by Facebook’s engineering team, this term is not interchangeable with React Native. React is a library mainly focused on web interface creation, while React Native refers to mobile development.
The biggest convenience of this framework is that programmers use a single code base to build apps for different platforms, which results in great savings not only in time but also in costs. At present, the framework is used by plenty of renowned companies including Uber, Instagram, Oculus, Coinbase, Walmart, and others.
The key features of the React Native Android framework:
- One codebase that can be run anywhere
- A live reload, which allows you to see the recent changes by refreshing the app
- RN uses modular programming that makes it easy to integrate updates
- React Native is an open-source framework
- Built by Meta Platforms, RN enjoys a trusted reputation
Flutter
Released in 2017, Flutter has managed to gain an excellent reputation and is considered as one of the most popular and powerful frameworks to build apps for devices with different OS. Maintained by Google and powered by Dart, the open-source software development tool creates applications using one codebase.
Flutter’s user interface engineering is built on widgets that form two groups: Material Design, which uses Google design, and Cupertino, which imitates iOS design. Additionally, Flutter features a “hot reload” function that allows seeing the modifications without even restarting the application.
The top features of the Flutter Android framework:
- It doubles your speed to market
- Cross-platform development approach that saves time and money
- Capacity to develop complex widgets
Ionic
Employing HTML, CSS, Angular, and JavaScript, Ionic technology is focused on hybrid mobile apps for Android, iOS, and Windows devices. Created by Drifty Co. in 2013, Ionic has built a large active mature community consisting of 5 million developers worldwide who have created 5 million Ionic-based apps.
Command Line Interface boasts a plethora of helpful commands and the most essential feature is its LiveReload, which aims to update the app instantly whenever any modification is made. Ionic seamlessly integrates with Angular, React, Vue, or can be used with no framework at all. With Ionic, engineers receive a library of plugins and a variety of UI components including cards, buttons, pop-ups, lists, segments, input fields, etc., thereby enabling faster UI development.
The main characteristics of the Ionic Android framework:
- Ionic creates products that run on multiple mobile operating systems
- Easily integrates with other libraries, frameworks, or used standalone
- A great number of plug-ins that allow engineers to use the functions of smartphones
- Certified by Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Xamarin
Another framework that is worth your attention is Xamarin, which is open-source and designed to build apps for Android, iOS, and Windows with NET. The Xamarin platform is targeted at developers who work with the C# language and create cross-platform applications. With this framework, you write one code for business logic that is used across different platforms but build separately specific versions of a user interface for each target platform.
The framework is capable of invoking Objective-C, Java, C, and C++ libraries to take advantage of existing code. There is no need to switch between the environments, and therefore engineers use Visual Studio both on Mac or Windows for app development. For the Android app, it’s needed to install the Java and Android SDKs.
The distinctive features of the Android Xamarin framework:
- Given the quality of UX, Xamarin apps look like native on any device
- To make the process of testing simpler, faster, and time-saving, the framework offers technology in the cloud as well as Xamarin Test Recorder
- Xamarin library boasts over 40 cross-platform layouts for different devices
- Developers can use a single API for all mobile platforms
NativeScript
Beloved by many front-end developers, NativeScript is a robust and widely-used framework that is applied for native app development. To ensure the high performance of applications and give users a native experience, the multi-cross platform employs such technologies as JavaScript, Angular, and TypeScript, which adds object-oriented programming capabilities to JS.
NT provides engineers with convenient methods to build a user interface as they can choose common UI components or create a unique one. To get started learning the basics of the framework, you can try NativeScript Playground, a cloud platform, to develop simple apps without installing various SDKs. If you wish to launch applications for different OS in the most cost-effective possible way, then NativeScript would be a great choice.
The key characteristics of the Android NativeScript framework:
- The development process involves technologies many engineers already know
- A great number of templates and plugins for features
- Provide access to all types of Android and iOS APIs
- Easily adaptable
Summing up
Today, there are many Android frameworks with plenty of specific features that you can take advantage of while developing a mobile app. However, bear in mind that every project has a different requirement, and so the choice of the framework must be made carefully and after checking the programming languages and the set of technologies your developers know.
The framework is the key component for building a successful mobile application that can greatly enhance your development experience. Therefore, it’s crucial to explore the main characteristics of the Android frameworks to find the most appropriate one that will help your mobile development projects end up being absolutely fantastic.














