Such research and scientific companies as Deloitte, McKinsey, and Accenture make predictions about healthcare technologies that will change the future of medicine. Although their estimates are slightly different, they agree on the main thing: innovations such as AI, VR, IoMT and telecommunications will affect the development of the industry in the first place. Leading healthcare software development companies are already delivering the most amazing software solutions for healthcare providers. Let’s take a look at the six most promising healthcare IT projects in 2022.
AI-based medical IT projects
Medical practitioners and researchers have high hopes for artificial intelligence in diagnosing and treating diseases. Forbes, Accenture, and McKinsey experts note that this technology has become the basis for smart image analysis, robotic surgery, improving chatbots, strengthening cybersecurity and personalizing medicine. Therefore, it is not surprising that Statista estimates that by 2025 the size of the global market will grow by almost 19 times compared to 2017.
AI for drug discovery from Verge Genomics
With the help of AI algorithms, medical organizations are trying to collect and analyze valuable data for medical research. So, Verge Genomics is working on an AI project that will accelerate the development and production of drugs to fight Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
However, there are certain difficulties. Every year pharmaceutical companies spend millions of dollars on drug testing. In the end, only 10-20% of medicines are allowed to be manufactured. Moreover, organizations need to spend an average of 12 years and $1.3 billion to conceive a drug, obtain FDA approval and successfully launch it on the market. People with fatal neurodegenerative diseases don’t have time to wait that long.
Verge Genomics decided to speed up drug discovery by developing an algorithm that can identify the most successful drug compounds. The company has created the world’s largest database of brain tissue sequences. Based on this data, AI identifies successful combinations of substances that are more likely to receive FDA approval and enter the market. The algorithm is looking for methods to “turn off” not minor genes, but an important gene that is responsible for the disease. In the future, it will allow treating not 5% of patients, but 95%.
AI to check test results
With the spread of COVID-19, medical organizations began to look for ways to stop the pandemic. Applications for contact tracing, safe travel, coronavirus quarantine monitoring and others have appeared. Medical organizations are mainly interested in how to facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of diseases using healthcare technologies.
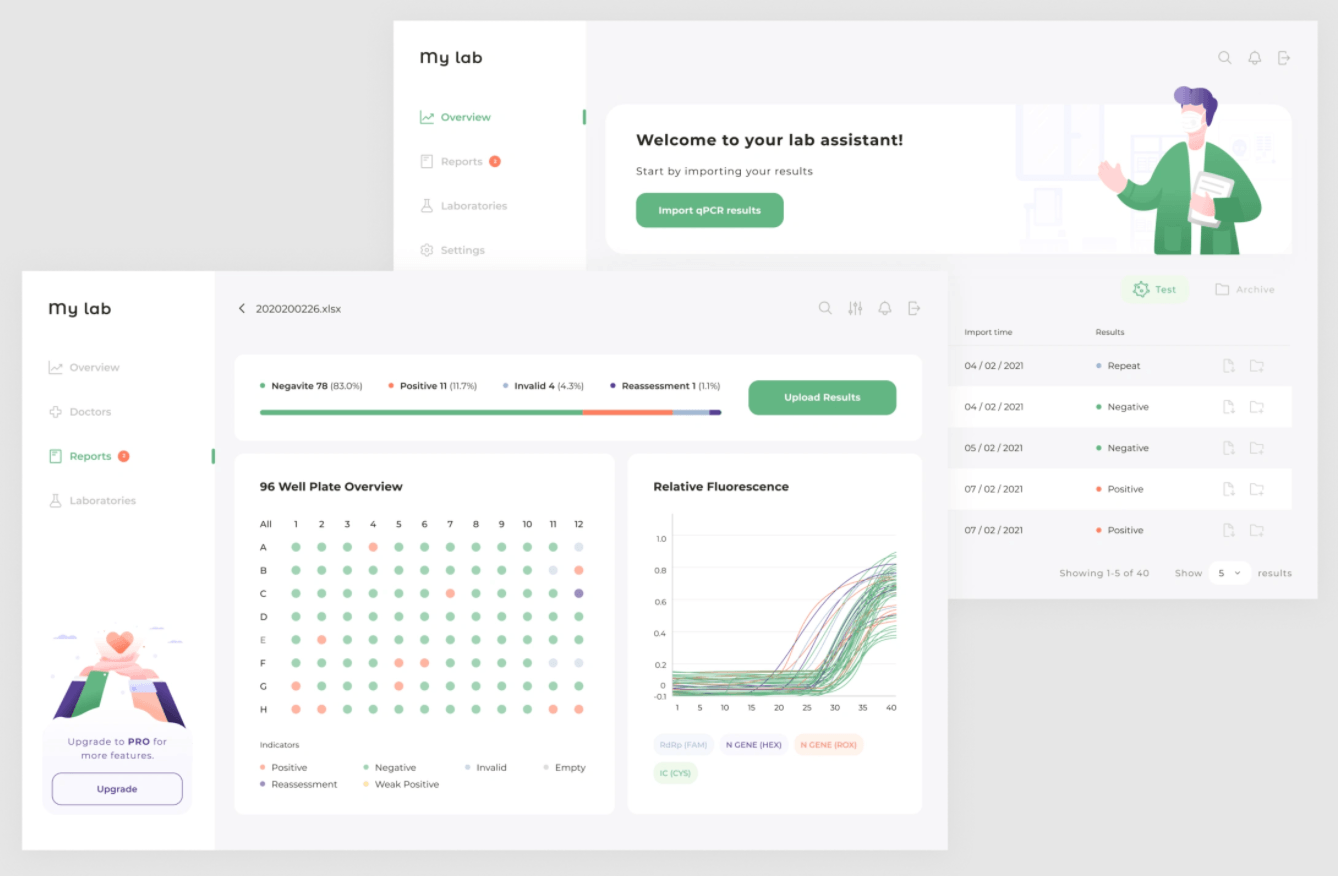
For example, Andersen has implemented a smart platform for a medical laboratory to check test results for COVID-19. An AI algorithm scans raw PCR results and analyzes information from laboratory machines of different models. AI processes the data; the platform displays the results on the dashboard and creates reports.
A laboratory assistant can only check the results and confirm them. If the employee doubts some reports, they manually review the PCR data and correct them. Such “edits” are rare because the algorithm was trained on tens of thousands of test results. The platform operates around the clock, leaving clinicians in control of the process. The system checks 96 tests per minute, so the productivity of the laboratory increases without sacrificing quality.
Screenshot of the platform
Source: Andersen
AR and VR projects
Statista estimates that the VR and AR industry will grow from $477 million in 2018 to $4.64 billion in 2025. The interest of medical organizations in immersive technologies is growing. VR and AR have proven themselves efficient in training doctors, treatment of mental disorders, rehabilitation of patients with disorders of the musculoskeletal system, and robotic surgery. Tech giants and startups are looking to make the most of immersive technology for healthcare needs.
Brain-computer interface by VRsano
Using VR technology, the American startup VRsano has created a brain-computer interface. The device combines three different methods of treatment: immersive, clinical hypnosis and neurofeedback. VRsano relieves patients of pain after major operations and helps them to cope with stress and anxiety. In this way, therapeutic 3D environments can be created for patients with ADD/ADHD, PTSD, migraines, depression, or other cognitive impairments.
Glasses or a VR headset immerse a patient in an alternative world with pleasant scenery and sounds. Healthcare technology helps a person with severe pain to take their mind off discomfort and refocus on something positive. The VR headset is connected to a computer through special software that broadcasts natural landscapes and game actions. The developers say that the brain-computer interface helps patients to recover 1.6-2 days faster than with traditional treatment.
Fighting burnout with Rescape Innovation
In 2021, about 70% of doctors complained of professional burnout, which is 30% more than in 2018. Researchers are raising the alarm: excessive fatigue, depression, and stress are becoming major problems for doctors, which ends in suicide in 22% of cases.
The British startup Rescape Innovation understands the criticality of the situation, so it has created a hardware-software solution to the problem – DR.VR. It is a Class 1 medical device – VR glasses to relieve stress in hospitals and clinics. An early prototype underwent quality assessment by Cwm Taf Morgannwg University Health Board and was approved by experts.
The device offers a 6-week relaxation course, created according to the methodology of psychologists specializing in well-being. During a session, doctors learn how to deal with stress and anxiety, adopt breathing practices and take relaxation exercises. DR.VR immerses medical professionals in pleasant places of interest, from an African safari to a deserted beach.
IoMT-based telemedicine projects
During the pandemic, healthcare has realized how important it is to use telecommunications technology and medical wearables to prevent the spread of the disease. Clinics and hospitals have begun to actively introduce telemedicine applications into medical practice.
Statista recorded an almost fourfold growth in the telemedicine market, from $50 billion in 2019 to an estimated $194 billion in 2023. A lot of HealthTech startups have appeared, striving to create comfortable conditions for remote treatment of patients who cannot or do not want to visit clinics for various reasons.
Andersen TeleMedicine tool
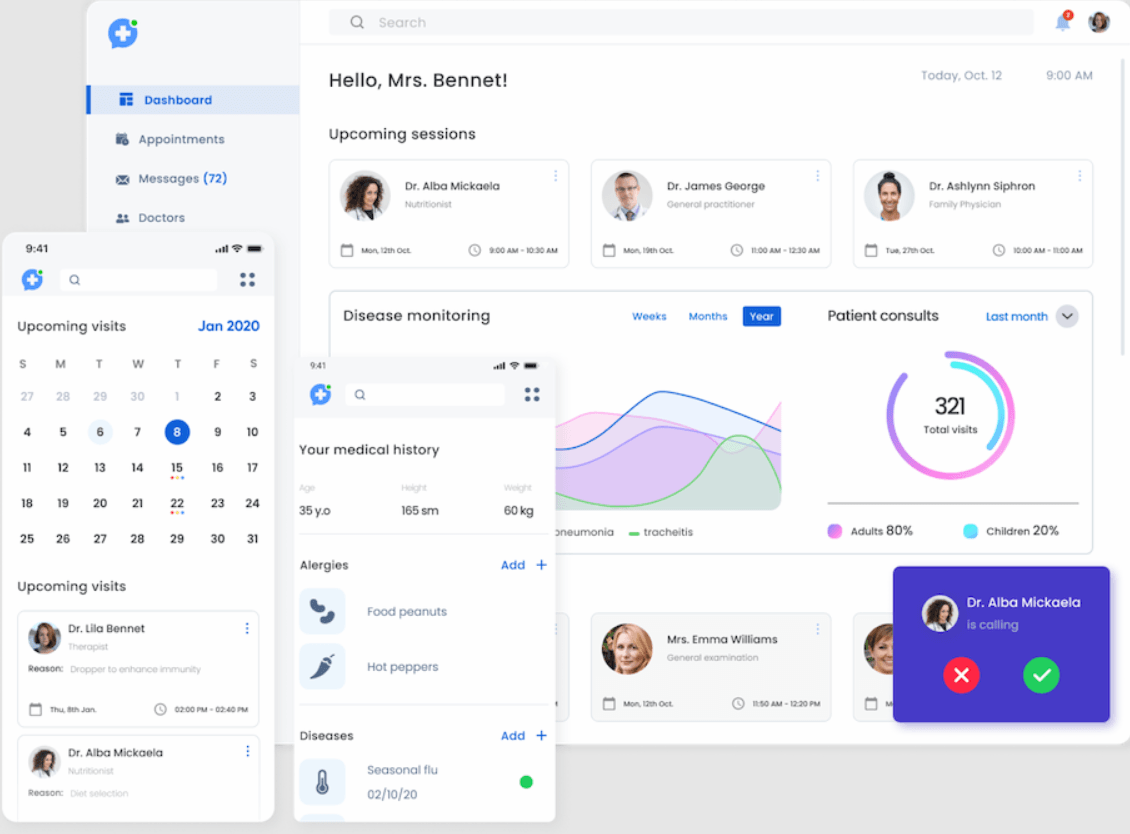
With the onset of the pandemic, an American healthcare facility implemented the TeleMedicine platform for remote patient monitoring. It includes emergency communication tools for smartphones and computers. The app integrates with the hospital’s EMR so the doctor can view a specific patient’s medical history through the platform.
The system can be connected to wearable devices (fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, ECG devices) so that the doctor collects statistics on the course of the disease and initiates a meeting with the patient when important vital signs deteriorate. The patient remotely books a visit to the doctor via video or telephone. The system warns of the scheduled appointment. If the doctor needs additional documents, test results or images, the patient simply transmits them via a secure encrypted communication channel.
Thus, the medical institution managed to increase the number of virtual visits to 46%, reduce cases of coronavirus infection, and improve the quality and timeliness of medical services.
Screenshot of the TeleMedicine platform
Source: Andersen
Tele-ICU by Ceiba
The American startup Ceiba is trying to solve one of the problems of the intensive care unit – the lack of doctors. The developers have created a universal telemetry solution that collects information from patient monitors, blood gas analyzers, ventilators and other sensors on a medical computer or smartphone. If a patient’s state deteriorates, the platform sounds an alarm through any device, including smartphones and wearables. The platform does not depend on technical devices, so there is no need to buy expensive equipment.
Tele-ICU facilitates day and night shifts for staff in intensive care units, surgery, LTACHs and other facilities. Patients are under control 24/7, even when there are not enough specialists in the department. Ceiba monitors the vital signs of a patient, evaluates the impact of medications, and analyzes the results of laboratory tests. In some cases, a doctor can remotely “treat” patients from another hospital.
Conclusion
We live in an amazing time when technology-driven healthcare is approaching the peak of its capabilities. What seemed fantasy twenty years ago is now becoming commonplace, largely due to promising healthcare IT projects and startups. Patients obtain better and more affordable treatments, medicines, and healthcare services. Healthcare thus reaches a new level and helps more people to defeat serious diseases. These are the reasons why the digital health market is skyrocketing. It is expected to grow from $175 billion in 2019 to $660 billion by 2025. And such prospects are truly encouraging.